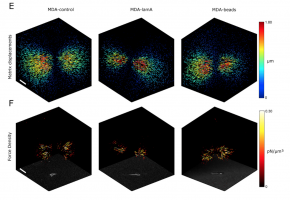
Cell migration through the extracellular matrix is governed by the interplay between cell-generated propulsion forces, adhesion forces, and resisting forces arising from the steric hindrance of the matrix. Steric hindrance in turn depends on matrix porosity, matrix deformability, cell size, and cell deformability. In this study, we investigate how cells respond to changes in steric hindrance that arise from altered cell mechanical properties. Specifically, we measure traction forces, cell morphology, and invasiveness of MDA-MB 231 breast cancer cells in three-dimensional collagen gels. To modulate cell me- chanical properties, we either decrease nuclear deformability by twofold overexpression of the nuclear protein lamin A or we introduce into the cells stiff polystyrene beads with a diameter larger than the average matrix pore size. Despite this increase of steric hindrance, we find that cell invasion is only marginally inhibited, as measured by the fraction of motile cells and the mean invasion depth. To compensate for increased steric hindrance, cells employ two alternative strategies. Cells with higher nuclear stiffness increase their force polarity, whereas cells with large beads increase their net contractility. Under both condi- tions, the collagen matrix surrounding the cells stiffens dramatically and carries increased strain energy, suggesting that increased force polarity and increased net contractility are functionally equivalent strategies for overcoming an increased steric hindrance.
Read the full article in Biophysical Journal.